Your tissue can heal faster after treatment by focusing on key recovery factors. You'll want to boost blood circulation through gentle exercise like walking or swimming, while keeping injured areas elevated above heart level. Stay well-hydrated and eat nutrient-rich foods, especially those high in protein, vitamins, and minerals. Avoid harmful substances like nicotine and excessive alcohol that restrict blood flow. Getting adequate rest, changing positions regularly, and maintaining proper wound care all support your body's natural healing mechanisms. Understanding how oxygen and blood flow work together opens up even more ways to speed up your recovery process.
Blood Flow Enhancement Fundamentals
The success of tissue healing largely depends on adequate blood flow to affected areas. You'll need to focus on several key techniques to enhance circulation and speed up your recovery process.
By elevating injured areas above your heart level, especially for lower extremities, you're helping your body improve venous return and reduce swelling.
Your diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy blood flow. You should consume foods rich in circulation-boosting nutrients like berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish.
Staying well-hydrated is equally important, as low blood volume can slow down your healing process. You'll want to avoid substances that constrict your blood vessels, such as nicotine, excessive caffeine, and alcohol, as they can substantially impair circulation.
Physical activity is essential for enhancing blood flow to healing tissues. You don't need to engage in intense exercise – even gentle movement can stimulate circulation. Simple exercises like toe wiggles and circles can effectively promote blood flow in your feet and legs.
If you're less mobile, you'll benefit from changing positions every 1-2 hours to prevent pressure points and maintain good blood flow. Compression garments can also help by applying gentle pressure that promotes better circulation throughout affected areas.
Oxygen Transport Mechanisms
Your body's blood flow distribution networks branch into increasingly smaller vessels until they reach the capillaries, where oxygen transport becomes critical for tissue healing.
Oxygen moves from these capillaries to cells through both passive diffusion and active convective transport in the interstitial fluid, with the latter being particularly important in damaged tissues. During the healing process, convective transport pumps over 100 times more oxygen into tissue than passive diffusion alone.
When you're healing, specialized oxygen-sensing mechanisms regulate this process while emerging technologies like oxygen-releasing hydrogels can help boost oxygen delivery to oxygen-starved areas.
Blood Flow Distribution Networks
Blood vessels form intricate distribution networks that deliver essential oxygen and nutrients during tissue repair. You'll find these vessels growing in specific patterns, with parallel formations in the superficial dermis and vertical arrangements in deeper tissue layers.
This organized network structure guarantees the best distribution of resources throughout the healing area. Platelet aggregation and activation trigger the release of growth factors that stimulate blood vessel formation.
The density of blood vessels directly impacts healing speed – the more vessels present, the faster oxygen and nutrients can reach damaged tissue. Upper and lower dermal plexuses play a critical role in restoring skin microcirculation, which is essential for successful wound healing.
You can monitor this process through advanced techniques like LDA, LSCI, and MED, which measure blood perfusion and track new vessel formation.
During healing, you'll see distinct phases where blood flow changes markedly. It starts with hemostasis (vasoconstriction), moves through inflammation (increased vascular permeability), and continues to the proliferative phase where new blood vessels form.
This network development supports re-epithelialization and wound maturation, creating a strong foundation for tissue repair. Understanding these distribution patterns helps healthcare providers enhance treatment strategies and monitor healing progress effectively.
Cellular Oxygenation Pathways
Oxygen's journey through healing tissues follows complex cellular pathways that determine repair success. When oxygen reaches your damaged tissues, it triggers multiple mechanisms that accelerate healing. It's not just about getting oxygen to the site – it's about how your cells utilize it for repair.
Your cells respond to proper oxygenation by increasing their proliferation rates and producing essential growth factors. Inside your tissues, oxygen enables specific enzymes to stabilize collagen, creating stronger structural support through molecular cross-linking. Studies show that wounds treated with oxygen-releasing hydrogels achieve closure much faster than untreated wounds.
You'll find that sustained oxygen levels also help reduce inflammation and manage oxidative stress.
What's particularly interesting is how your cells use oxygen to power their energy production. With adequate oxygen, your cells can generate more ATP, fueling the intensive work of tissue repair.
The oxygen activates vital signaling pathways, including Erk1/2 and HO-1, which keep your cells alive and metabolically active. It's also involved in epigenetic regulation, turning on genes that were previously silent but are needed for healing.
Through specialized delivery systems like blood vessels and therapeutic oxygen-releasing microspheres, your tissues receive the continuous supply they need to regenerate effectively.
Cellular Regeneration Pathways
Several intricate cellular signaling pathways orchestrate the complex process of tissue regeneration. You'll find that the JNK pathway at the wound's center acts as a vital organizer, while spatial separation of JNK and JAK/STAT pathways controls cell fusion and proliferation. The MAPK pathway, when activated by antioxidants like NAC, boosts progenitor cell growth.
| Pathway | Function | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| JNK | Wound organization | Coordinates regeneration |
| JAK/STAT | Cell regulation | Controls fusion events |
| MAPK | Growth promotion | Enhances proliferation |
| Stem Cell | Tissue repair | Enables multipotency |
| Fibroblast | Matrix production | Supports wound closure |
Your body's regenerative capacity relies heavily on various cell types working together. Stem cells and tissue-resident progenitors become multipotent after injury, while fibroblasts transform into myofibroblasts to close wounds. You'll notice that circulating cells from your bone marrow help form new blood vessels, and local stem cells activate repair mechanisms in skin appendages. Modern treatments can enhance these natural processes through gene therapy, bioengineered scaffolds, and advanced dressings that manage the wound environment effectively.
Tissue Recovery Process
The process of tissue recovery unfolds through distinct phases that work in harmony to restore damaged areas. Your body first enters the inflammation phase, which typically lasts several days as your immune system cleans up debris and fights potential infections. During this time, you'll likely notice typical signs of inflammation like swelling and redness.
As inflammatory cells begin to die off, you'll enter the proliferation phase, which can continue for several weeks. In this phase, your body forms new blood vessels and granulation tissue to rebuild the damaged area.
Next comes the remodeling phase, where you'll see the formation of scar tissue – a process that can span months or even years.
The final maturation phase strengthens your new tissue, but it won't begin until about two months after injury, and complete maturation can take years. Your recovery timeline depends heavily on factors like your age, overall health, and lifestyle choices.
If you have conditions like diabetes or you smoke, you'll likely experience slower healing. You can support faster healing through proper nutrition, regular wound care, and following your healthcare provider's treatment plan.
Healing Time Optimization
Optimizing your tissue's healing time involves multiple key factors working together. You'll need to maintain the right moisture balance while ensuring proper blood flow and oxygenation to the affected area.
Your body's healing process works most efficiently when you're providing adequate nutritional support, particularly through sufficient protein intake.
Key strategies to accelerate your healing include:
- Creating a moist wound environment that promotes cell migration
- Removing any dead or damaged tissue promptly
- Using advanced dressings that actively support the healing process
- Maintaining ideal nutrition and hydration levels
If you're dealing with more complex wounds, you'll benefit from newer technologies like bioengineered scaffolds and cellular products. These solutions can markedly boost your healing response, though they may come at a higher cost.
Don't overlook the importance of controlling bacterial growth and managing systemic conditions like diabetes that could slow your recovery. For surgical wounds, early intervention and proper graft selection are vital.
You'll achieve the best results by combining these approaches with consistent wound care and appropriate physical therapy when needed. Remember that proper oxygenation and blood flow to the wound site remain fundamental to quick healing.
Light Therapy Benefits
Light therapy stands as a powerful ally in tissue healing, offering multiple scientifically-proven benefits for wound recovery and repair. When you're looking to accelerate healing, light therapy stimulates dermal blood flow and promotes neovascularization, ensuring your damaged tissues receive the best possible oxygen and nutrients.
You'll experience reduced inflammation and pain as light therapy decreases inflammatory cells and swelling. It's particularly effective at enhancing cellular recovery by delivering concentrated energy deep into your tissues, where it stimulates fibroblasts to produce more collagen. This increased collagen synthesis strengthens your healing tissues and improves their final tensile strength.
What makes light therapy especially valuable is its ability to speed up epithelialization while supporting muscle regeneration. You'll find it accelerates keratinocyte proliferation, which is essential for wound closure and minimizing scarring.
Plus, it's completely safe and non-invasive, with no significant side effects.
Whether you're recovering from surgery, treating burns, or healing wounds, light therapy enhances your body's natural healing processes. It does this by reducing oxidative stress, improving ATP production, and supporting the activity of healing cells like neutrophils and lymphocytes.
Natural Healing Acceleration Methods

When seeking natural methods to accelerate tissue healing, understanding your body's innate repair mechanisms becomes essential. Your body moves through distinct healing phases, including bleeding, proliferation, and remodeling, each playing a critical role in tissue repair.
You'll find that supporting these natural processes can substantially speed up your recovery time.
Your body's healing mechanisms rely heavily on growth factors and proper blood flow. You can boost these natural processes through several evidence-based methods:
- Maintain healthy nutrition with protein-rich foods that provide building blocks for tissue repair
- Stay well-hydrated to support blood flow and cellular regeneration
- Get adequate sleep to allow your body's natural repair mechanisms to work efficiently
- Practice gentle movement within pain limits to stimulate blood flow to healing tissues
To maximize natural healing, you'll want to focus on activities that promote angiogenesis – the formation of new blood vessels. This process guarantees your healing tissues receive adequate oxygen and nutrients.
Research shows that controlled movement and proper nutrition can enhance your body's production of growth factors like PDGF and EGF, which are important for tissue regeneration and repair.
Recovery Time Reduction Techniques
Building on your body's natural healing processes, modern recovery techniques can dramatically reduce tissue repair time. Growth factor therapy, particularly using TGF-beta 1, enhances collagen synthesis and strengthens healing wounds. You'll find this especially effective when combined with advanced dressing technologies that deliver these growth factors directly to the injury site.
You can accelerate your recovery through targeted oxygen therapy and electromagnetic treatments. Topical wound oxygen therapy increases oxygen supply to damaged tissues, while pulsed electromagnetic therapy stimulates cellular growth. These methods work particularly well with active dressings that incorporate hydrogels, which provide sustained release of therapeutic agents.
For the best results, you'll want to evaluate pharmaceutical interventions like deoxyribonucleosides or recombinant growth factors. However, you'll need to carefully manage any anti-inflammatory medications, as they can slow down healing.
If you're on immunosuppressants or chemotherapy, you'll require specialized wound care approaches that include antimicrobial dressings to prevent infection. The latest thermoresponsive hydrogels and biomaterial scaffolds can support your tissue regeneration by promoting cell growth and blood vessel formation.
Blood Vessel Response
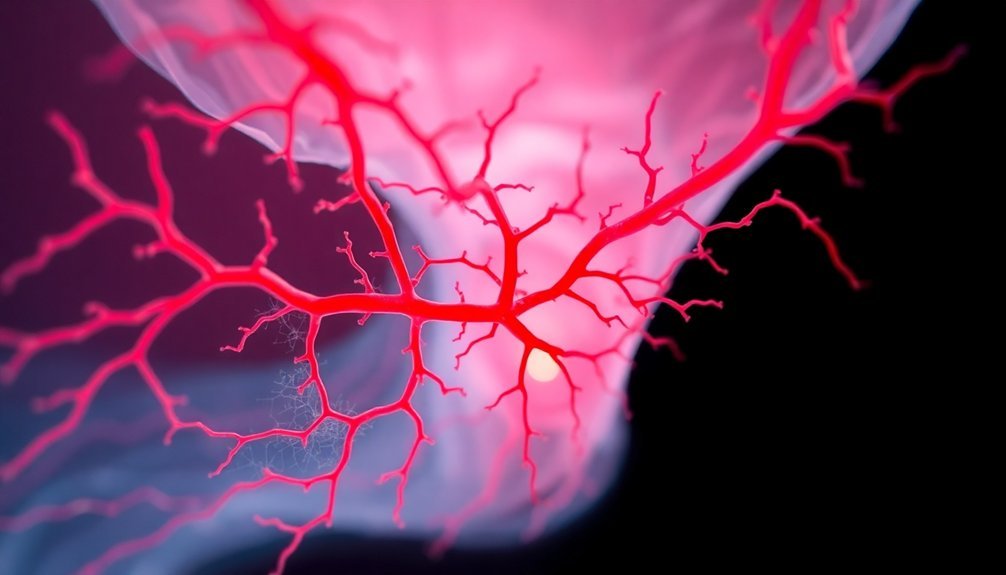
Your body's remarkable healing process relies heavily on the formation of new blood vessels through angiogenesis.
You'll see increased blood flow to the injured area as VEGF and other growth factors trigger existing blood vessels to sprout new branches, delivering essential oxygen and nutrients.
This targeted vascular response helps speed up your recovery by ensuring damaged tissues receive the resources they need to rebuild effectively.
Angiogenesis Drives New Growth
The formation of new blood vessels, known as angiogenesis, begins immediately after tissue injury through a complex cascade of events. When you're injured, platelets release essential growth factors like VEGF, PDGF, and TGF-β that kick-start this process.
These molecules work together to stimulate the growth and movement of endothelial cells, which form the building blocks of new blood vessels.
Your body's inflammatory response amplifies this process. Macrophages and monocytes release additional growth factors, while enzymes break down damaged tissue to clear the way for new vessel formation. You'll find that this carefully orchestrated process creates a network of new blood vessels that deliver essential oxygen and nutrients to healing tissues.
- Blood vessel sprouts emerge from existing vessels like tiny branches
- Endothelial cells form hollow tubes that extend and connect
- New vessels create an intricate web throughout the healing tissue
- The network gradually refines itself as healing progresses
As your tissue heals and oxygen levels return to normal, angiogenesis naturally slows down. Some of the newly formed vessels will regress, leaving behind a refined vascular network that supports your fully healed tissue.
Blood Flow Increases Healing
Inside your healing tissues, blood flow serves as the critical lifeline for recovery. Your blood vessels deliver essential oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products, creating the perfect environment for healing.
When you're injured, platelets in your blood immediately begin controlling bleeding and releasing growth factors that jumpstart the repair process.
You'll heal faster when you maintain good circulation through simple actions. Regular activities like walking or swimming can boost blood flow without straining your wound.
If you've had treatment, you'll want to keep the area elevated when possible to reduce swelling and improve circulation. You should also stay well-hydrated and maintain a nutritious diet to support your blood's ability to transport healing factors.
If you're dealing with chronic conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular disease, you'll need to pay extra attention to your circulation. These conditions can slow healing by compromising blood flow.
You might benefit from compression garments to manage swelling and enhance circulation. Remember to avoid smoking, as it constricts your blood vessels and impairs the healing process.
Through proper blood flow management, you're giving your body the best chance at efficient healing.
Tissue Oxygenation Principles
Maintaining ideal tissue oxygenation stands as a cornerstone principle in wound healing and tissue repair. When your tissues receive adequate oxygen levels, they can effectively produce collagen and grow new blood vessels, essential components for healing. You'll find that insufficient oxygen (hypoxia) substantially hinders the healing process, particularly in chronic wounds.
Your body's healing mechanism relies heavily on proper oxygen delivery and distribution. Here's what happens when oxygen reaches your damaged tissues:
- White blood cells use oxygen to fight infection through oxidative killing
- Cells interact with the surrounding matrix to rebuild tissue
- New blood vessels form to restore circulation
- Collagen production increases to strengthen the healing area
You can enhance tissue oxygenation through various therapeutic approaches, including hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) and supplemental oxygen during surgery.
It's vital to monitor tissue oxygen levels throughout treatment, as this helps healthcare providers adjust your care plan accordingly. Remember that too much or too little oxygen can affect healing outcomes, so finding the right balance is essential.
Combining oxygen therapy with other treatments, like compression to reduce swelling, often provides the best results.
Healing Factors and Stimulation
Multiple healing factors work together to promote successful tissue repair, with electrical stimulation (ES) emerging as a powerful therapeutic tool. You'll find that proper oxygenation, infection control, and nutrition are essential for your wound to heal effectively.
However, if you're dealing with conditions like diabetes, obesity, or smoking, they can substantially slow down your healing process.
ES can help overcome these challenges by enhancing your body's natural healing mechanisms. When you receive ES treatment, it increases blood flow, activates growth factors, and influences cellular movements in your damaged tissue.
You'll see improved tissue regeneration and faster wound closure as ES stimulates cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation.
Your medications can impact healing too. If you're taking cancer treatments, NSAIDs, anticoagulants, or immunosuppressants, they might slow down your recovery. That's why your healthcare provider needs a complete medication history to identify potential risks.
Clinical evidence shows that different types of ES, including high-voltage pulsed current and low-intensity direct current, can effectively treat both acute and chronic wounds, leading to reduced wound size and enhanced blood flow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Emotional Stress Affect How Quickly Tissues Heal After Injury?
Yes, your emotional stress substantially slows down tissue healing by increasing cortisol levels, which suppresses your immune system. You'll heal up to 40% slower when stressed, as shown in various clinical studies.
Does Regular Exercise Before Injury Influence Tissue Healing Speed?
Yes, if you've exercised regularly before getting injured, your tissues will heal faster. You'll benefit from better blood circulation, reduced inflammation, and enhanced oxygen delivery, all thanks to your pre-injury fitness routine.
How Do Different Sleeping Positions Impact Wound Healing Rates?
Back sleeping's your best option for wound healing as it reduces pressure and improves circulation. Side sleeping's acceptable with proper support, but you'll want to avoid stomach sleeping, which can restrict blood flow.
Can Music Therapy or Sound Frequencies Accelerate Tissue Healing?
Yes, you'll find that music therapy can speed up tissue healing by about 10%. It'll reduce your pain, lower stress hormones, and improve blood flow by regulating your heart rate and blood pressure levels.
Do Genetic Factors Significantly Influence Individual Tissue Healing Capabilities?
Yes, your genes substantially impact how quickly you heal. Your genetic makeup influences wound microbiome diversity, healing rates, and tissue repair processes through specific genes like TLN2, VEGF, and growth factor expression.
In Summary
You'll find that improving blood flow and oxygen delivery are key factors in speeding up tissue healing. By following proper treatment protocols, you're enhancing cellular regeneration and activating natural healing pathways. When you maintain good nutrition, stay hydrated, and get adequate rest, you're supporting your body's recovery process. Remember that patience is essential, as rushing the healing process won't lead to ideal results.





Leave a Reply