Different wavelengths of light penetrate your skin at varying depths, which directly impacts their healing potential. Red light (600-700 nm) works best for surface-level concerns, while near-infrared light (700-900 nm) reaches deeper tissue layers for enhanced therapeutic effects. You'll get the most benefit when the light makes direct contact with your skin, as this minimizes reflection and maximizes penetration power. The ideal treatment depends on your specific skin condition and target depth, with factors like skin thickness playing a vital role. Understanding these penetration patterns can reveal the full potential of light therapy for your needs.
Light Wavelengths Matter for Healing
Over the past decade, researchers have confirmed that specific light wavelengths play a pivotal role in the body's healing process. If you're seeking ideal healing results, you'll want to focus on near-infrared light (800-830 nm) and red light (630-680 nm), as these wavelengths have proven most effective for wound healing and tissue repair. Research from Defence Institute of Physiology consistently validates these findings.
You'll find that wavelength selection directly impacts how deep the light penetrates your skin. Near-infrared light reaches deeper tissue layers, while red light works effectively on more superficial areas. When you combine these wavelengths, you're getting a thorough treatment approach that can reduce inflammation and restore function across multiple skin layers.
The science shows that 904 nm superpulsed light also delivers significant photobiomodulatory effects for dermal wound healing.
When you're considering light therapy treatments, remember that penetration depth varies according to your skin's optical properties. This means the effectiveness of your treatment depends heavily on matching the right wavelength to your specific skin condition.
Skin Depth Determines Treatment Success
Understanding skin depth penetration is essential when you're selecting light-based treatments, as it directly influences therapeutic outcomes. Multiple factors affect how deeply light penetrates your skin, including wavelength, stratum corneum thickness, and the angle at which light hits your skin's surface. Research shows that wavelengths between 440-600 nanometers penetrate 1-2 millimeters into the skin.
| Treatment Type | Penetration Effect | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Ablative Fractional Laser | Deep penetration | Superior wrinkle reduction & elasticity |
| Bipolar Radiofrequency | Moderate penetration | Good elasticity improvement |
| Intense Pulsed Light | Variable penetration | Moderate wrinkle & elasticity results |
| Micro-Needling | Controlled depth | Excellent scar & texture improvement |
You'll need multiple sessions to achieve the best results, regardless of which treatment you choose. Scientific modeling, like Monte Carlo Radiative Transport, helps predict how different wavelengths will penetrate your skin layers. This knowledge guides treatment selection and optimization. For instance, if you're targeting deeper skin concerns, you'll want treatments with greater penetration capabilities. The thickness of your skin's outer layer (stratum corneum) also plays a significant role – thinner areas allow for better penetration, while thicker areas may require more intensive treatment approaches.
Penetration Power by Spectrum Range
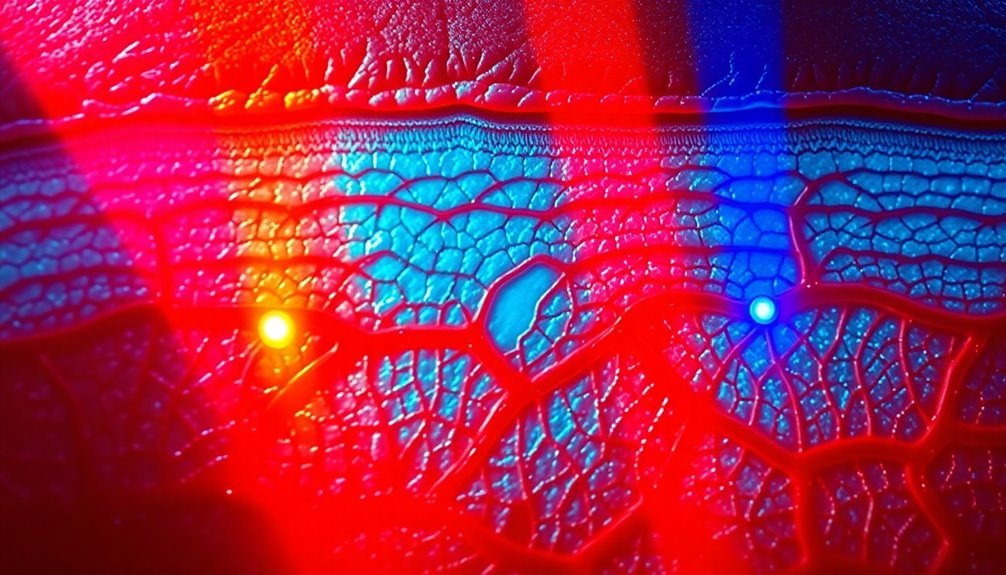

Light penetration varies dramatically across different spectrum ranges, with each wavelength offering unique therapeutic benefits and depth capabilities.
UV radiation primarily affects the skin's surface layers, with penetration highly dependent on wavelength and varying between 290-341 nm. The thinner your skin's stratum corneum, the deeper UV radiation can reach.
Red light (600-700 nm) penetrates more profoundly, reaching up to 1mm with 63% intensity. You'll find even more impressive results with red light at 660 nm, which can penetrate up to 21mm in specific tissue types. This wavelength range falls within the optical window where there's minimal absorption by melanin, hemoglobin, and water. Direct skin contact during treatment maximizes light transmission by reducing reflection and refraction losses.
Near-infrared light (700-900 nm) offers the deepest penetration, with 810 nm considered ideal due to minimal tissue absorption. You'll see penetration depths ranging from 2.4mm to 5mm, allowing NIR to reach deeper tissues like muscle and brain matter.
However, you should note that light intensity decreases substantially with depth, regardless of wavelength. This principle's essential for your treatment planning, as you'll need to account for both penetration depth and power loss when targeting specific tissue layers.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Blood Circulation Affect Light Penetration in Different Skin Layers?
Your blood-free epidermis allows easy light penetration, while blood vessels in your dermis increase scattering and absorption. In your hypodermis, circulation's effects are limited but still promote healing through nitric oxide production.
Can Medications or Topical Products Alter Skin's Wavelength Penetration Properties?
Yes, you'll find that chemical enhancers and medications can modify your skin's optical properties. They'll alter the stratum corneum's structure and hydration levels, which directly affects how different wavelengths penetrate your skin layers.
Does Age-Related Skin Thinning Impact the Effectiveness of Light-Based Treatments?
No, your age-related skin thinning won't substantially reduce light therapy's effectiveness. Red and infrared light can still penetrate effectively and stimulate collagen production, while laser treatments remain targeted regardless of skin thickness.
What Role Do Skin Conditions Like Eczema Play in Wavelength Penetration?
When you have eczema, your skin's inflammation and irregular barrier function can alter light penetration. You'll notice this affects treatment effectiveness, requiring careful adjustment of wavelengths, especially for UVB phototherapy treatments.
How Do Seasonal Changes in Skin Thickness Affect Light Therapy Results?
You'll notice reduced light therapy results in winter due to decreased skin hydration and thickness. In summer, your skin's increased moisture and thickness allows for better light penetration and more effective treatments.
In Summary
You've learned how different wavelengths of light penetrate your skin at varying depths, impacting treatment effectiveness. Understanding the relationship between light spectrum and tissue penetration will help you choose the right therapy for your needs. Whether you're seeking pain relief, skin rejuvenation, or wound healing, remember that wavelength selection directly determines how deep the therapeutic benefits will reach.





Leave a Reply